Diagnosing 6.0 Powerstroke Exhaust Gas Temperature Sensor Failure

Featured image for this comprehensive guide about Diagnosing 6.0 Powerstroke exhaust gas temperature sensor failure
Image source: guideabouthvac.com
Diagnosing 6.0 Powerstroke Exhaust Gas Temperature Sensor Failure
Ah, the 6.0 Powerstroke. A legendary engine to some, a notorious enigma to others. Regardless of where you stand, one thing is certain: keeping this powerhouse running optimally requires a keen eye on its intricate web of sensors. Among these, the exhaust gas temperature (EGT) sensor plays a crucial, often underappreciated role. When a 6.0 Powerstroke EGT sensor failure occurs, it doesn’t just trigger a dashboard light; it can throw off your engine’s performance, fuel economy, and even lead to more significant, costly damage.
Many owners experience the frustration of erratic engine behavior or persistent “Check Engine” lights without immediately identifying the root cause. This comprehensive guide is designed to empower you with the knowledge and actionable steps needed for diagnosing 6.0 Powerstroke EGT sensor failure. We’ll delve into the sensor’s function, explore common symptoms, decode relevant Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs), and walk you through a detailed diagnostic process to get your Powerstroke back on track. Let’s dive in and demystify the complexities of this vital component.
Quick Answers to Common Questions
What does the Exhaust Gas Temperature Sensor (EGT) do in my 6.0 Powerstroke?
This sensor is crucial for monitoring the temperature of your exhaust gases, providing vital data to the engine control module (ECM) for proper engine management and emission control.
What are the common signs of a bad EGT sensor in a 6.0 Powerstroke?
You might notice symptoms like a “check engine” light, reduced engine performance, increased fuel consumption, or unusual exhaust smells, all pointing towards a potential 6.0 Powerstroke exhaust gas temperature sensor failure.
Can a faulty EGT sensor cause other problems for my 6.0 Powerstroke?
Absolutely! An inaccurate reading from a bad sensor can lead to incorrect fuel trims, DPF issues, and potentially even engine damage if not addressed, making diagnosing 6.0 Powerstroke exhaust gas temperature sensor failure crucial.
How can I quickly check if my 6.0 Powerstroke’s EGT sensor is working?
A quick check often involves using an OBD-II scanner to look for specific diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) related to the EGT circuit. You can also monitor live data to see if the temperature readings are plausible.
Is it safe to drive my 6.0 Powerstroke with a suspected EGT sensor failure?
While you might be able to drive it, it’s not recommended for long. Driving with a failed EGT sensor can lead to further issues and potential costly repairs down the line, so diagnosing and addressing 6.0 Powerstroke exhaust gas temperature sensor failure promptly is best.
📋 Table of Contents
- The Critical Role of the 6.0 Powerstroke EGT Sensor
- Common Symptoms of a Failing 6.0 Powerstroke EGT Sensor
- Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) Related to EGT Sensor Failure
- Step-by-Step Diagnosis: Pinpointing the 6.0 Powerstroke EGT Sensor Issue
- Preventing EGT Sensor Failure and Maintenance Tips
- Repair and Replacement Considerations
- Conclusion
The Critical Role of the 6.0 Powerstroke EGT Sensor
Before we can diagnose problems, it’s essential to understand what the exhaust gas temperature sensor does and why it’s so critical for your 6.0 Powerstroke. This seemingly small component is a silent guardian, constantly monitoring the thermal conditions within your exhaust system.
Learn more about Diagnosing 6.0 Powerstroke exhaust gas temperature sensor failure – Diagnosing 6.0 Powerstroke Exhaust Gas Temperature Sensor Failure
Image source: sc01.alicdn.com
What is an EGT Sensor and How Does It Work?
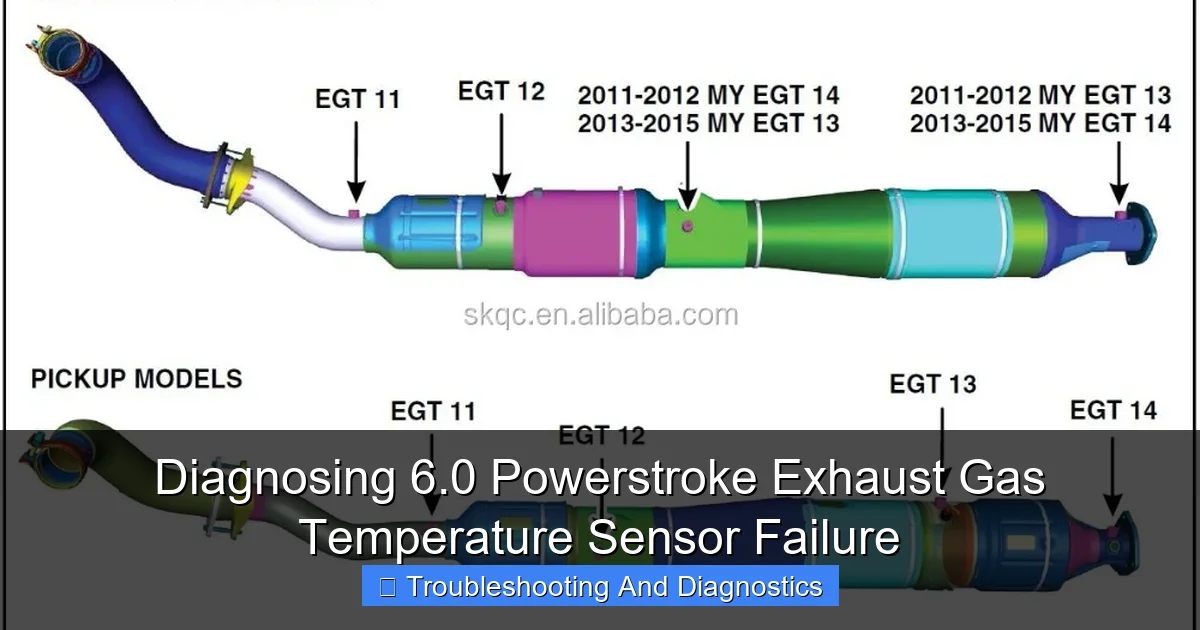
An EGT sensor is essentially a thermocouple, a device that measures temperature. In your 6.0 Powerstroke, it’s typically located in the exhaust stream, often before or after the catalytic converter and/or diesel particulate filter (DPF). It measures the temperature of the exhaust gases as they exit the engine. This temperature data is then converted into an electrical signal and sent to the Powertrain Control Module (PCM).
| Diagnostic Test/Observation | Normal EGT Sensor Behavior (Expected) | Indication of EGT Sensor Failure | Related DTCs / Common Symptoms |
|---|---|---|---|
| **Scan Tool Live Data (Key On Engine Off – KOEO / Cold Engine)** | EGT reading closely matches Ambient Air Temp (AAT) or Engine Coolant Temp (ECT). | Fixed very low (-40°F/-40°C), fixed very high (e.g., 1200°F/650°C), or “Not Available”. | P0544, P0546, P2031, P2033 (EGT Circuit High/Low/Range). |
| **Scan Tool Live Data (Engine Warm / Idling)** | EGT gradually increases from ambient, stabilizes around 250-450°F (120-230°C). | Reading remains at ambient, erratic fluctuations, or stuck at a fixed extreme value. | P0544, P0546, P2031, P2033, reduced engine power/performance. |
| **Wiring & Connector Inspection** | Wiring intact, connector clean, no signs of chafing, melting, or corrosion. | Frayed/burnt wires, corroded pins, damaged insulation, melted connector plastic. | Intermittent EGT-related DTCs, Check Engine Light, potential short/open circuit. |
| **Sensor Resistance Test (Sensor Disconnected, Ohms)** | Resistance changes smoothly with temperature (e.g., ~150-250 kOhms cold, decreasing significantly when heated for NTC thermistors). | Open circuit (OL), short circuit (0 Ohms), or fixed resistance that doesn’t change with heat. | P0544 (EGT Circuit High/Open), P0546 (EGT Circuit Low/Short). |
| **Engine Performance / EGR Function** | Smooth acceleration, proper Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) operation. | Reduced power, excessive smoke, poor fuel economy, disabled EGR, engine derate. | P0404 (EGR performance), P0299 (underboost) – often indirect results of incorrect EGT data. |
The PCM uses this real-time EGT data for several critical functions, acting as the brain that interprets the signals to make crucial adjustments to engine operation. Without accurate EGT readings, the PCM is essentially flying blind, leading to a cascade of potential issues.
Why is the EGT Sensor So Important for the 6.0 Powerstroke?
The 6.0 Powerstroke’s EGT sensor is vital for:
- Engine Protection: Extremely high exhaust temperatures can damage vital engine components, especially the turbocharger and exhaust valves. The PCM uses EGT data to adjust fuel delivery and turbocharger operation to prevent overheating, safeguarding your engine from severe thermal stress.
- Emissions Control: Modern diesel engines, including the 6.0 Powerstroke, rely heavily on precise exhaust temperature management for effective emissions control. The EGT sensor ensures that catalytic converters and DPFs operate within their optimal temperature windows for efficient pollutant reduction.
- DPF Regeneration: For 6.0 Powerstrokes equipped with a Diesel Particulate Filter (DPF) (though less common on early models, later ones might have retrofit or specific applications), accurate EGT readings are paramount for initiating and controlling the DPF regeneration process. Regeneration burns off accumulated soot, and if EGT readings are incorrect, the DPF might not regenerate effectively, leading to clogging and reduced performance.
- Fuel Economy & Performance: The PCM utilizes EGT data to fine-tune fuel injection timing and quantity, as well as turbo boost pressure. Inaccurate EGT readings can lead to suboptimal engine tuning, resulting in reduced fuel efficiency and a noticeable drop in power.
- Diagnostic Integrity: The EGT sensor is part of a complex feedback loop. When it fails, the PCM can’t accurately assess exhaust conditions, leading to false readings or generic fault codes that make accurate diagnosis of other issues challenging.
Common Symptoms of a Failing 6.0 Powerstroke EGT Sensor
Recognizing the symptoms of a failing exhaust gas temperature sensor 6.0 Powerstroke is the first step in successful diagnosis. These symptoms can range from subtle annoyances to significant performance issues. Pay close attention to these indicators:
Learn more about Diagnosing 6.0 Powerstroke exhaust gas temperature sensor failure – Diagnosing 6.0 Powerstroke Exhaust Gas Temperature Sensor Failure
Image source: theinstrumentguru.com
- Illuminated Check Engine Light (CEL): This is arguably the most common and immediate sign. The PCM detects an abnormal signal from the EGT sensor and triggers the CEL, often accompanied by a specific Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC).
- Reduced Engine Performance or “Limp Mode”: When the PCM receives unreliable EGT data, it might enter a protective “limp mode,” significantly reducing engine power and limiting RPMs to prevent potential damage. You’ll notice a distinct lack of acceleration and overall responsiveness.
- Poor Fuel Economy: Inaccurate EGT readings can cause the PCM to over-fuel or under-fuel the engine, leading to inefficient combustion. This directly translates to more frequent trips to the fuel pump.
- Excessive Exhaust Smoke: If the engine is over-fueling due to incorrect EGT data, you might observe increased black smoke from the exhaust, especially under acceleration.
- Failed Emissions Test: An improperly functioning EGT sensor can disrupt the emissions control system, leading to higher-than-acceptable pollutant levels and a failed emissions inspection.
- Rough Idle or Stalling: While less common and often indicative of multiple issues, an EGT sensor providing wildly inaccurate data can sometimes contribute to unstable idle conditions or even stalling, as the PCM struggles to maintain optimal engine parameters.
- DPF Regeneration Issues (if applicable): If your 6.0 Powerstroke has a DPF, a faulty EGT sensor can prevent proper regeneration cycles, leading to DPF clogging, reduced power, and eventually a DPF-related CEL.
- Unusual Odors from Exhaust: A rich-running condition due to EGT sensor failure can sometimes produce a strong, acrid smell from the exhaust.
It’s important to remember that some of these symptoms can overlap with other engine problems. Therefore, proper diagnosis, starting with checking for DTCs, is crucial.
Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) Related to EGT Sensor Failure
When your 6.0 Powerstroke EGT sensor fails, the PCM is designed to detect the anomaly and store specific Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs). These codes are your primary clues for pinpointing the exact nature of the problem. Using an OBD-II scanner is the most direct way to retrieve these codes.
Common EGT Sensor DTCs for the 6.0 Powerstroke:
The 6.0 Powerstroke may have multiple EGT sensors in various locations (e.g., pre-turbo, post-turbo, pre-DPF, post-DPF). The specific code will often indicate the bank and sensor number. Here are some of the most common codes you might encounter:
- P0428: Catalyst Temperature Sensor Circuit High Input (Bank 1 Sensor 1) – Often refers to an EGT sensor reporting excessively high temperatures.
- P0429: Catalyst Temperature Sensor Circuit Low Input (Bank 1 Sensor 1) – Indicates an EGT sensor reporting excessively low temperatures or an open circuit.
- P042A / P042B / P042C / P042D / P042E / P042F: These codes are generally related to EGT sensor circuit performance or range issues for specific exhaust temperature sensors, usually followed by an indicator for “Bank 1 Sensor 1” or “Bank 1 Sensor 2,” etc. For instance, P042A might be for “Exhaust Gas Temperature Sensor 1 Circuit,” and P042B for “Exhaust Gas Temperature Sensor 1 Circuit Range/Performance.”
- P0430 – P043F: Similar to the P042x series, but typically referring to Bank 2 (if applicable, though 6.0 Powerstrokes are usually single bank exhaust systems for this purpose, but it’s good to be aware of the pattern).
- P2031, P2032, P2033: Exhaust Gas Temperature Sensor Circuit Bank 1 Sensor 2 (P2031 – circuit, P2032 – low, P2033 – high). These refer to the second EGT sensor in the exhaust stream.
- P2080, P2081: Exhaust Gas Temperature Sensor Circuit Range/Performance Bank 1 Sensor 1 (P2080) or intermittent/erratic (P2081).
Understanding the DTCs:
When you retrieve a code, pay close attention to the specific wording provided by your scanner. A code like “P042D: Exhaust Gas Temperature Sensor Circuit High Bank 1 Sensor 2” tells you not only that there’s an issue with an EGT sensor, but also its approximate location and the nature of the electrical fault (high voltage, indicating a short or incorrect resistance reading). Always consult your vehicle’s specific service manual for the most accurate interpretation of these codes, as interpretations can vary slightly between models and years.
Common EGT-Related DTCs and Their Meanings
| DTC Code | Common Description | Potential Cause of EGT Sensor Failure |
|---|---|---|
| P0428 | Catalyst Temperature Sensor Circuit High Input (Bank 1 Sensor 1) | Sensor shorted to voltage, open circuit, or internal sensor failure reading high. |
| P0429 | Catalyst Temperature Sensor Circuit Low Input (Bank 1 Sensor 1) | Sensor shorted to ground, open circuit, or internal sensor failure reading low. |
| P042A | Exhaust Gas Temperature Sensor 1 Circuit | General electrical fault in Sensor 1 circuit (wiring, connector, or sensor). |
| P042B | Exhaust Gas Temperature Sensor 1 Circuit Range/Performance | Sensor reading outside expected parameters, likely internal sensor degradation. |
| P2031 | Exhaust Gas Temperature Sensor Circuit Bank 1 Sensor 2 | General electrical fault in Sensor 2 circuit (often downstream of DPF). |
| P2032 | Exhaust Gas Temperature Sensor Circuit Low Bank 1 Sensor 2 | Sensor 2 reporting low temperatures, open circuit, or short to ground. |
| P2033 | Exhaust Gas Temperature Sensor Circuit High Bank 1 Sensor 2 | Sensor 2 reporting high temperatures, short to voltage, or open circuit. |
| P2080 | Exhaust Gas Temperature Sensor 1 Circuit Range/Performance | Sensor 1 providing inconsistent or implausible readings. |
Step-by-Step Diagnosis: Pinpointing the 6.0 Powerstroke EGT Sensor Issue
Once you’ve identified potential symptoms and retrieved DTCs, it’s time to get hands-on with diagnosing 6.0 Powerstroke EGT sensor failure. This section will guide you through a systematic approach to confirm the problem.
Preliminary Checks
Before diving into electrical testing, perform these simple visual checks:
- Visual Inspection: Locate the EGT sensor(s) in your exhaust system. Look for any obvious physical damage to the sensor itself, such as cracks, corrosion, or impact damage.
- Wiring Harness & Connectors: Carefully inspect the wiring leading to the EGT sensor. Look for frayed wires, pinched sections, melted insulation, or signs of rodent damage. Check the electrical connector for corrosion, bent pins, or a loose connection. A common culprit for intermittent issues is a poorly seated or corroded connector.
- Exhaust Leaks: Although not directly causing EGT sensor failure, an exhaust leak upstream of the sensor can cause inaccurate readings by allowing cooler ambient air to mix with exhaust gases, leading to false low-temperature signals.
Essential Tools for Diagnosis
To accurately diagnose a faulty 6.0 Powerstroke exhaust gas temperature sensor, you’ll need a few key tools:
- OBD-II Scan Tool: Essential for reading DTCs and, critically, monitoring live data streams. A professional-grade scanner that can read manufacturer-specific parameters will be most helpful.
- Digital Multimeter (DMM): For measuring voltage, resistance (ohms), and continuity.
- Heat Gun / Propane Torch (with caution): For safely applying heat to the sensor during bench testing (only if removed).
- Wiring Diagram: Specific to your 6.0 Powerstroke year/model, to identify correct wire colors and pinouts.
Detailed Diagnostic Procedure
Follow these steps for a thorough diagnosis:
- Retrieve and Record DTCs: As mentioned, this is your starting point. Note down all present and pending codes. Clear the codes and see if they immediately return after starting the engine.
- Monitor Live Data (Crucial Step):
- Connect your OBD-II scanner and navigate to the live data stream.
- Locate the “Exhaust Gas Temperature” (EGT) parameter(s). You might see multiple, labeled as EGT11, EGT12, etc., corresponding to Bank 1 Sensor 1, Bank 1 Sensor 2, and so on.
- With the engine cold (ignition on, engine off), all EGT sensors should read approximately ambient air temperature. If one sensor reads significantly different (e.g., -40°F/C or an extremely high temperature like 2300°F/1260°C), it’s a strong indicator of an open or short circuit, or an internal sensor failure.
- Start the engine and observe the EGT readings as the engine warms up. All sensors should show a gradual and relatively consistent increase in temperature. A sensor that remains stuck at a low temperature, drops to zero, or spikes to an implausible high temperature (e.g., over 1500°F/815°C under normal driving) is likely faulty.
- If you have multiple EGT sensors, compare their readings. While they won’t be identical, they should follow similar trends. A significant divergence between sensors is a red flag.
- Resistance Testing (Sensor Out of Vehicle):
- Disconnect the battery for safety. Carefully remove the EGT sensor from the exhaust pipe.
- Set your multimeter to measure resistance (ohms).
- Measure the resistance across the two pins of the EGT sensor connector. Consult a service manual for the expected resistance values at specific temperatures. Generally, EGT sensors are NTC (Negative Temperature Coefficient) thermistors, meaning resistance decreases as temperature increases.
- You can use a heat gun or carefully apply heat with a propane torch (from a distance, briefly) to the sensor tip while observing the resistance change. Resistance should decrease smoothly as heat is applied and increase as it cools. If there’s no change, or the change is erratic, the sensor is bad.
- A typical EGT sensor might have resistance ranging from ~200,000 ohms when cold to ~500 ohms when very hot.
- Voltage Checks (At the Connector, Engine Off/On):
- With the ignition on (engine off) and the EGT sensor disconnected, back-probe the harness connector that leads to the PCM. You’re looking for reference voltage (usually 5V) and ground.
- Refer to your wiring diagram to identify the signal wire, reference voltage wire, and ground wire.
- You should typically find a 5-volt reference signal from the PCM on one wire and a good ground on another. The signal wire will fluctuate.
- If you don’t have the correct voltage or ground, the issue might be with the wiring harness or the PCM itself, not the sensor.
- Continuity Test (Wiring Harness):
- If you suspect a wiring issue, disconnect the EGT sensor at both ends (from the sensor and from the PCM connector, if accessible).
- Use your multimeter to check for continuity between the corresponding pins at each end of the harness. There should be continuity (very low resistance).
- Also, check for continuity between each wire and a known good ground, and between adjacent wires (looking for shorts). Any continuity where there shouldn’t be indicates a short circuit.
By systematically following these diagnostic steps, you should be able to confidently pinpoint whether your 6.0 Powerstroke exhaust gas temperature sensor is indeed faulty or if the problem lies elsewhere in the electrical circuit.
Preventing EGT Sensor Failure and Maintenance Tips
While some failures are inevitable due to component lifespan, understanding the common causes of 6.0 Powerstroke EGT sensor failure and adopting proactive maintenance habits can significantly extend its life and prevent future headaches.
Common Causes of EGT Sensor Failure
- Thermal Cycling and Stress: EGT sensors operate in an extremely harsh environment, constantly exposed to rapid and extreme temperature changes. This continuous heating and cooling can lead to material fatigue and eventual failure.
- Vibration: The constant vibrations from the engine and exhaust system can loosen internal components or cause wiring to chafe and break.
- Corrosion and Contamination: Exposure to exhaust gases, moisture, road salt, and other contaminants can lead to corrosion on the sensor tip or electrical connections, degrading performance or causing complete failure.
- Physical Damage: Impact from road debris, improper handling during other repairs, or even excessively rough off-road driving can physically damage the sensor or its wiring.
- Age and Mileage: Like any electronic component, EGT sensors have a finite lifespan. As your 6.0 Powerstroke accumulates mileage and years, the likelihood of sensor degradation increases.
- Engine Performance Issues: Underlying engine problems that cause excessively high EGTs (e.g., clogged injectors, improper tuning) can prematurely stress and fail EGT sensors.
Best Practices for EGT Sensor Longevity
Here’s how you can help prolong the life of your 6.0 Powerstroke EGT sensor:
- Regular Visual Inspections: During oil changes or other routine maintenance, take a moment to visually inspect the EGT sensors and their wiring. Look for obvious signs of damage, corrosion, or loose connections.
- Maintain a Healthy Exhaust System: Ensure your exhaust system is free of leaks, which can expose sensors to external elements or incorrect temperature readings. Secure exhaust hangers can also reduce vibration.
- Address Engine Issues Promptly: Don’t ignore symptoms of poor engine performance. Issues like clogged fuel injectors, a failing turbo, or improper tuning can lead to excessive exhaust temperatures, putting undue stress on the EGT sensors.
- Use Quality Replacement Parts: When a replacement is necessary, opt for high-quality OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) or reputable aftermarket sensors. While cheaper options exist, they often have a shorter lifespan and can lead to recurring problems.
- Proper Installation: When replacing an EGT sensor, ensure it’s installed correctly, with appropriate anti-seize compound (if recommended by the manufacturer) and torqued to specifications. Overtightening can damage the sensor.
- Protect Wiring: Ensure all wiring harnesses are properly secured and away from hot or sharp components to prevent chafing or melting.
Proactive maintenance and prompt attention to symptoms can significantly reduce the chances of sudden 6.0 Powerstroke EGT sensor failure, saving you time and money in the long run.
Repair and Replacement Considerations
Once you’ve confirmed a 6.0 Powerstroke EGT sensor failure, the next step is replacement. This isn’t a particularly complex job for most DIYers, but choosing the right part and following proper installation procedures are key to a successful repair.
Choosing the Right Replacement Sensor
- OEM vs. Aftermarket: While OEM (Ford/Motorcraft) sensors are generally recommended for their guaranteed fit and quality, reputable aftermarket brands (like Bosch, Denso, or parts from trusted diesel specialists) can offer a good balance of quality and cost. Avoid no-name or unusually cheap sensors, as they often have a high failure rate.
- Application Specificity: Ensure the sensor you purchase is specifically designed for your exact year and model of 6.0 Powerstroke and its intended location (e.g., pre-turbo, post-DPF, if applicable). There are subtle differences in resistance curves and connector types.
Installation Tips for the 6.0 Powerstroke EGT Sensor
Replacing an exhaust gas temperature sensor 6.0 Powerstroke involves a few key steps:
- Safety First: Ensure the engine is cool before working on the exhaust system. Disconnect the negative battery terminal to prevent accidental shorts and resets.
- Locate the Sensor: Based on your diagnosis and the DTC, identify the correct sensor to replace.
- Disconnect Electrical Connector: Carefully unclip the electrical connector. Often, these have locking tabs that need to be squeezed or lifted. Avoid pulling on the wires.
- Remove Old Sensor: Use an appropriate oxygen sensor or EGT sensor socket (often a specialized deep socket with a slit for the wire) to loosen and remove the old sensor. Exhaust components can be stubborn, so a penetrating oil (like PB Blaster) applied beforehand can help significantly.
- Apply Anti-Seize: Crucially, apply a high-temperature anti-seize compound to the threads of the new sensor. This will prevent it from seizing in the exhaust pipe due to heat and corrosion, making future removal much easier.
- Install New Sensor: Hand-thread the new sensor into the exhaust pipe to ensure it doesn’t cross-thread. Then, use your socket to tighten it to the manufacturer’s specified torque. Do not overtighten.
- Reconnect Electrical Connector: Ensure the connector clicks securely into place.
- Reconnect Battery and Clear Codes: Reconnect the negative battery terminal. Use your OBD-II scanner to clear all stored DTCs.
Post-Replacement Verification
After replacing the 6.0 Powerstroke exhaust gas temperature sensor:
- Test Drive: Take your truck for a thorough test drive, including varying speeds and loads, to allow the PCM to relearn and confirm proper operation.
- Monitor Live Data: Use your scan tool to monitor the EGT readings for the newly installed sensor. Ensure it’s reporting temperatures that are consistent with other sensors (if present) and that it responds logically to engine temperature changes.
- Check for Recurring Codes: After the test drive, re-scan for DTCs to ensure no new or old codes have reappeared.
By following these steps, you’ll ensure a proper repair and restore your 6.0 Powerstroke to its optimal operating condition, free from the issues caused by a faulty EGT sensor.
Conclusion
The exhaust gas temperature sensor might be a small component in the grand scheme of your 6.0 Powerstroke, but its role in engine management, emissions control, and overall performance is undeniably significant. Ignoring the signs of a 6.0 Powerstroke EGT sensor failure can lead to a cascade of problems, from reduced fuel economy and diminished power to potentially severe engine damage and costly repairs.
By understanding the symptoms, decoding Diagnostic Trouble Codes, and following our detailed step-by-step diagnostic and repair procedures, you are now equipped to tackle diagnosing 6.0 Powerstroke EGT sensor failure with confidence. Proactive maintenance, choosing quality replacement parts, and meticulous installation are your best defenses against future issues. Keep a vigilant eye on your dashboard, listen to your engine, and act swiftly when symptoms arise. Your reliable 6.0 Powerstroke will thank you with many more miles of powerful, efficient performance.
🎥 Related Video: 🚨 DPF Blockage Alert: Faulty Exhaust Temperature Sensor Detected 🚨 💨 #ytshorts #car #ford #dpf
📺 Life Behind Cars
Where is the front airbag crash sensor on a Alfa Romeo Giulietta Lusso Jtdm-2 Diesel 2011 1956cc.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common symptoms of a failed 6.0 Powerstroke exhaust gas temperature sensor?
A failing exhaust gas temperature sensor (EGT sensor) can trigger a “Check Engine” light, often accompanied by specific diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) like P2031, P040X, or P0544. You might also notice reduced engine performance, poor fuel economy, or the vehicle entering a reduced power mode to protect critical components.
How can I confirm if my 6.0 Powerstroke exhaust gas temperature sensor is truly faulty?
The most reliable way is to use an OBD-II scanner to read live data from the EGT sensor. Compare its reported temperature with known good values or a reliable external thermometer (if accessible) in similar conditions. A sensor showing abnormally high, low, or stuck readings (e.g., -40°F or +2500°F) is a strong indicator of failure.
Where is the exhaust gas temperature sensor typically located on a 6.0 Powerstroke?
On a 6.0 Powerstroke, there can be multiple exhaust gas temperature sensors, but the primary one for diagnosis is often located in the exhaust stream, either pre-turbo, post-turbo, or sometimes within the exhaust manifold. Its precise location can vary slightly depending on the model year and emission system configuration.
Can I continue to drive my 6.0 Powerstroke if I suspect an exhaust gas temperature sensor failure?
While the truck might still run, it’s not recommended to drive for extended periods with a failed exhaust gas temperature sensor. Incorrect EGT readings can lead to the PCM making poor fueling decisions, potential engine damage from overheating, or issues with the exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) system and turbocharger longevity.
Will a failing 6.0 Powerstroke exhaust gas temperature sensor always trigger a “Check Engine” light?
Yes, in most cases, a fault with the exhaust gas temperature sensor will trigger the “Check Engine” light and store a specific diagnostic trouble code (DTC) in the powertrain control module (PCM). These codes are crucial for pinpointing the exact sensor or circuit issue that needs attention.
What are common causes of 6.0 Powerstroke exhaust gas temperature sensor failure?
EGT sensors are exposed to extreme heat and corrosive exhaust gases, making them prone to degradation over time. Common causes of failure include carbon buildup on the sensor tip, internal element breakdown due to thermal stress, wire harness damage from heat or vibration, and sometimes even physical impact.






