Replaced Camshaft Position Sensor But Still Get Code? [Solved]
The engine control module (ECM) is a complex system that relies on various sensors to ensure optimal performance and fuel efficiency in modern vehicles. One such sensor is the camshaft position sensor (CMP), which plays a crucial role in synchronizing engine operation and monitoring valve timing. When a fault occurs in this component, it can trigger an error code and result in engine performance issues.
Replacing a faulty camshaft position sensor is often the go-to solution when confronted with a persistent error code. However, it can be frustrating and perplexing when the error code remains even after the replacement. What could be causing this dilemma? Are there other potential culprits that need to be addressed?
In this blog post, we will delve into the complexities of camshaft position sensor issues and explore the possible reasons behind the persisting error code. We will discuss additional troubleshooting steps that can help you pinpoint the root cause and provide insights to guide you towards a successful resolution. So, let’s dive in and unravel the mysteries surrounding these stubborn error codes.
What Error Codes Show By Camshaft Position Sensor Problems?
When the camshaft position sensor (CMP) encounters issues, it can trigger various error codes, indicating problems with the sensor or its related components. Some of the common error codes associated with camshaft position sensor problems include:
1. P0340 (Camshaft Position Sensor Circuit Malfunction):
Are there any other potential causes for the P0340 error code?
Yes, there are other potential causes for the P0340 error code, such as circuit problems, a faulty starter motor, or lingering fault codes that may not clear immediately after sensor replacement. It is advisable to drive the vehicle for a reasonable distance to allow the ECM to relearn and reassess the sensor’s operation.
What are the suggested steps to solve the problem, such as disconnecting the battery or clearing the codes with an OBD2 scanner?
To solve the problem, suggested steps include disconnecting the battery for 10 minutes to reset the system or clearing the codes with an OBD2 scanner. This can help to resolve issues related to the error code and potentially clear it.
What are the possible issues with the wiring, camshaft position sensor reluctor wheel, or the new sensor itself that can lead to the persistent error code?
Issues with the wiring, such as damaged or loose connections, can interfere with the proper transmission of signals and result in persistent error codes. A damaged camshaft position sensor reluctor wheel or a defective new sensor can also contribute to the persistent error code.
What are the specific reasons for the error code to persist even after replacing the camshaft position sensor?
The error code may persist even after replacing the camshaft position sensor due to issues with the wiring or connector associated with the sensor, incorrect alignment or improper installation of the new sensor, underlying problems with other components connected to the sensor, the need for ECM reprogramming, or the ECM taking time to reevaluate the sensor’s performance and clear the codes on its own.
What are the potential causes of the P0340 error code?
The potential causes of the P0340 error code include problems with the wiring, camshaft position sensor reluctor wheel, or if the new camshaft position sensor is incompatible or has a factory defect.
2. P0341 (Camshaft Position Sensor Circuit Range/Performance): This code typically suggests that the camshaft position sensor is not providing the expected signal range or performance. It may be due to a faulty sensor, improper installation, or a problem with the timing belt.
3. P0345 (Camshaft Position Sensor A Circuit Malfunction): This error code specifically points to a malfunction in the Camshaft Position Sensor “A” circuit. It could be caused by a faulty sensor, wiring issues, or a problem with the ECM.
4. P0349 (Camshaft Position Sensor “A” Circuit Intermittent): This code indicates intermittent connectivity issues in the Camshaft Position Sensor “A” circuit. It may be caused by loose or damaged wiring, a faulty sensor, or poor electrical connections.
These are just a few examples of the error codes related to camshaft position sensor problems. It’s important to note that the specific error codes may vary depending on the vehicle make, model, and year.

What Does P0340 Error Code Means?
The P0340 error code is a generic diagnostic trouble code (DTC) that indicates a malfunction in the camshaft position sensor (CMP) circuit. This code is often displayed as “Camshaft Position Sensor Circuit Malfunction.”
When the ECM (engine control module) detects a problem with the camshaft position sensor circuit, it triggers the P0340 error code. The camshaft position sensor is responsible for monitoring the position and speed of the camshaft, which helps the ECM determine the precise timing of the engine’s valve operation.
Possible causes of the P0340 error code include:
1. Faulty camshaft position sensor: The sensor itself may be malfunctioning, providing incorrect readings or no signal at all.
2. Wiring issues: Damaged or loose wiring connections between the sensor and the ECM can disrupt the signal transmission.
3. Sensor alignment: If the camshaft position sensor is not properly aligned or installed, it may not accurately detect the camshaft’s position.
4. Timing belt or chain problems: A worn-out or misaligned timing belt or chain can affect the camshaft’s position, leading to the error code.
5. ECM issues: In rare cases, a problem with the engine control module itself can cause the P0340 error code.
What other potential causes can lead to the P0340 error code?
In addition to the camshaft position sensor issues, other potential causes of the P0340 error code include wiring issues, sensor alignment problems, and timing belt or chain issues. Rarely, a problem with the engine control module itself can also cause the error code.
What specific issues can occur with the camshaft position sensor?
The camshaft position sensor itself may be defective or malfunctioning, providing incorrect readings or no signal at all.
Can a faulty starter motor cause the P0340 error code?
Yes, a faulty starter motor can potentially cause the P0340 error code.
What is the role of the camshaft position sensor reluctor wheel?
The camshaft position sensor reluctor wheel can become damaged and affect the accuracy of the sensor’s readings, leading to the P0340 error code.
What are the circuit problems that can cause the P0340 error code?
Circuit problems with the sensor’s electrical connector or wiring can cause the P0340 error code.
Does the P0340 error code cause loss of power while driving?
Yes, loss of power while driving is one of the symptoms associated with the P0340 error code.
Does the P0340 error code cause misfires?
Yes, misfires are one of the symptoms of the P0340 error code.
Does the P0340 error code cause bad fuel economy?
Yes, bad fuel economy is one of the symptoms of the P0340 error code.
Does the P0340 error code cause rough idling?
Yes, rough idling is one of the symptoms associated with the P0340 error code.
Does the P0340 error code cause the check engine light to come on?
Yes, the check engine light will come on as one of the symptoms of the P0340 error code.
To diagnose and resolve the P0340 error code, it is recommended to perform a thorough inspection of the camshaft position sensor and its circuitry. This may involve checking the sensor’s connections, testing the sensor’s functionality, and verifying the timing belt or chain’s condition.
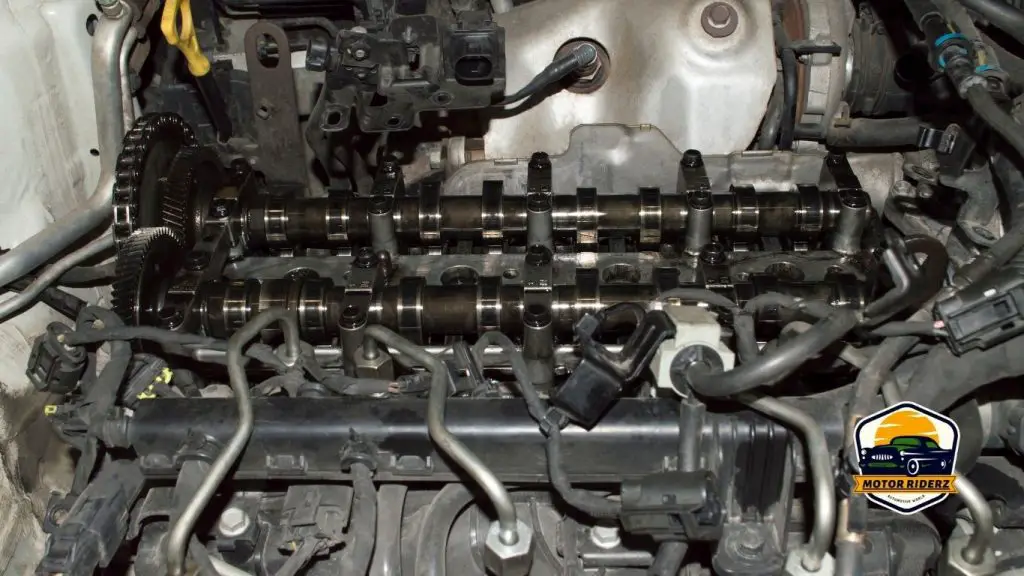
Why Are You Still Getting Code After Replacing Camshaft Position Sensor?
Replacing the camshaft position sensor (CMP) is typically the first step in resolving issues related to the sensor or its circuit. However, there are several reasons why you might still be getting error codes even after replacing the sensor. Here are some possible explanations:
1. Wiring or connector issues
The problem may lie in the wiring harness or connector associated with the camshaft position sensor. Damaged, corroded, or loose connections can interfere with the proper transmission of signals, resulting in persistent error codes.
2. Sensor alignment or installation
Incorrect alignment or improper installation of the new camshaft position sensor can lead to continued error codes. It is crucial to ensure that the sensor is aligned correctly and securely fastened in its designated position.
3. Related components
While the camshaft position sensor is a common culprit for error codes, there might be underlying issues with other components connected to the sensor. Problems with the timing belt/chain, reluctor wheel, or the engine control module (ECM) itself can cause recurring error codes even after sensor replacement.
4. ECM reprogramming
Some vehicles require the ECM to be reprogrammed or have the error codes cleared after sensor replacement. Failure to perform this step can result in the persistence of the codes.
5. Lingering fault codes
The error codes may not clear immediately after sensor replacement. The ECM may take some time to reevaluate the sensor’s performance and clear the codes on its own. It is advisable to drive the vehicle for a reasonable distance to allow the ECM to relearn and reassess the sensor’s operation.
How To Get Rid Of This Code?
If you are dealing with a persistent error code related to the camshaft position sensor (CMP), here are seven steps you can follow to try and resolve the issue:
1. Double-check the installation: Ensure that the new camshaft position sensor is correctly aligned and securely installed. Verify that all connections are tight and free from any damage or corrosion.
2. Inspect the wiring harness: Carefully examine the wiring harness connected to the camshaft position sensor. Look for any signs of frayed wires, loose connections, or damaged insulation. Repair or replace any faulty wiring as necessary.
3. Clear the error codes: Use an OBD-II scanner or code reader to clear the error codes from the ECM’s memory. This step is crucial as it allows the system to reevaluate the sensor’s performance without any lingering codes.
4. Test the sensor signal: Use a multimeter or oscilloscope to test the camshaft position sensor’s signal output. Compare the readings to the manufacturer’s specifications. If the signal is erratic or outside the acceptable range, it may indicate a faulty sensor that needs to be replaced again.
5. Check the reluctor wheel: Inspect the reluctor wheel that interacts with the camshaft position sensor. Ensure that it is clean, properly aligned, and free from any damage. A damaged or misaligned reluctor wheel can cause inaccurate sensor readings.
6. Verify timing belt/chain condition: Examine the condition of the timing belt or chain. Look for signs of wear, stretching, or misalignment. A worn-out or improperly functioning timing belt/chain can affect the camshaft’s position, leading to error codes. Replace the timing belt/chain if necessary.
7. Consult a professional mechanic: If you have followed the previous steps and are still unable to resolve the issue, it is advisable to seek assistance from a professional mechanic or dealership. They have specialized knowledge, tools, and diagnostic equipment to accurately diagnose and repair complex camshaft position sensor problems.

What will happen if differential fluid is never changed?
If differential fluid is neglected and not changed regularly, the consequences can be problematic. With the passage of time, the differential fluid begins to deteriorate, leading to increased wear and tear on the gears within the differential. This deterioration can occur due to the accumulation of dust, dirt, and metal particles that contaminate the fluid. As a result, the gears, bearings, and other moving components of the differential may wear out prematurely.
The differential plays a crucial role in powering the wheels when you make turns. It is positioned at the back of the vehicle and consists of intricate gears and bearings. As the differential fluid degrades, it loses its ability to properly lubricate and cool these components. Without adequate lubrication, the gears can experience excessive friction and heat, leading to accelerated wear.
Ultimately, if differential fluid is never changed, the gears within the differential are more likely to wear out faster than they should. This can result in costly repairs or even total failure of the differential. Regularly changing the differential fluid helps maintain optimal performance, prevent premature wear, and ensure the longevity of the differential and its components.
FAQ:
1. How Long Do Camshaft Position Sensors Last?
Camshaft position sensors typically have a lifespan of around 100,000 to 150,000 miles (160,000 to 240,000 kilometers). However, their longevity can be influenced by various factors, including driving conditions, engine design, and the quality of the sensor itself. Over time, the sensor may experience wear and tear, leading to decreased performance or failure. Regular maintenance and timely replacement of the camshaft position sensor when necessary can help ensure optimal engine performance and prevent potential issues. It is always recommended to refer to the vehicle manufacturer’s guidelines and consult a professional mechanic for specific recommendations regarding sensor replacement intervals.
2. Can I Drive With A Camshaft Position Sensor Problem?
It is generally not advisable to drive with a faulty camshaft position sensor. A malfunctioning sensor can negatively impact engine performance, fuel efficiency, and overall drivability. It may cause issues such as rough idling, stalling, poor acceleration, or even engine misfires. Additionally, continued driving with a faulty sensor can lead to further damage to other engine components. It is recommended to address camshaft position sensor problems promptly by having the sensor inspected, repaired, or replaced to ensure safe and reliable vehicle operation.
3. How Much Does It Cost To Replace The Camshaft Position Sensor?
“The cost of replacing a camshaft position sensor can vary depending on several factors, including the make and model of your vehicle, the location of the sensor, and labor costs in your area. On average, the cost for parts alone can range from $50 to $200. Labor costs typically add to the total expense, which can range from $50 to $150 or more, depending on the complexity of the replacement process. It’s always a good idea to consult with a mechanic or service center to get an accurate estimate for your specific vehicle and location.
That being said, it is important to note that the average cost of replacing a camshaft position sensor falls within the range of $100 to $200. This is a fairly inexpensive repair in comparison to other automotive maintenance tasks. However, it is essential to consider that the actual cost may vary based on the unique circumstances surrounding your vehicle.
Factors such as the make and model of your car will influence the availability and pricing of the replacement sensor. Additionally, the location of the sensor within your vehicle can affect the complexity of the replacement process, which can in turn impact the overall labor costs involved. Lastly, labor rates can vary from one area to another, so it is advisable to reach out to a qualified mechanic or service center in your vicinity for a precise estimate.
By taking into account these various factors, you can gain a better understanding of the cost range associated with replacing a camshaft position sensor. It is always recommended to consult with a professional to get an accurate estimate tailored to your specific vehicle and location.”
4. What Should You Do After Replacing The Camshaft Sensor?
After replacing the camshaft position sensor, it is recommended to perform the following steps:
1. Clear error codes: Use an OBD-II scanner or code reader to clear any existing error codes from the ECM’s memory.
2. Test drive: Take the vehicle for a test drive to ensure that the new sensor is functioning correctly and that the error codes do not reappear.
3. Monitor performance: Pay attention to the engine’s performance, including idle smoothness, acceleration, and any signs of abnormal behavior. If you notice any issues, consult a professional mechanic for further diagnosis.
4. Keep records: Document the date and mileage of the sensor replacement for future reference and maintenance records.
5. Can You Replace A Camshaft Position Sensor Yourself?
Yes, in many cases, you can replace a camshaft position sensor yourself. The level of difficulty may vary depending on the specific vehicle make and model. It is important to consult the vehicle’s service manual for instructions tailored to your vehicle. Assess your mechanical skills and ensure you have the necessary tools.



One Comment
Comments are closed.