How to Fix 7.3 Powerstroke Fuel Injector Circuit Issues: Diagnostic Guide

Featured image for this comprehensive guide about How to fix 7.3 Powerstroke fuel injector circuit issues
Image source: i0.wp.com
Ah, the legendary 7.3 Powerstroke! For many, it’s more than just an engine; it’s a way of life. Known for its robust reliability and undeniable torque, this diesel workhorse has powered countless trucks through millions of miles. However, even legends have their Achilles’ heel, and for the 7.3, one of the most common and frustrating challenges can be its fuel injector circuit. When your beloved Powerstroke starts acting up – sputtering, misfiring, or refusing to start altogether – the culprit often lies within these intricate electrical pathways.
Diagnosing 7.3 Powerstroke fuel injector circuit issues can feel like chasing ghosts. Is it a bad injector? A faulty wiring harness? A temperamental Injector Driver Module (IDM)? The complexity can quickly become overwhelming, leading to expensive guesswork and unnecessary parts replacements. But fear not, fellow diesel enthusiast! This comprehensive guide is designed to arm you with the knowledge, tools, and step-by-step procedures to confidently pinpoint and fix these pesky problems, saving you time, money, and a lot of headaches.
We’ll delve deep into the heart of your 7.3’s injection system, unraveling its components and common failure points. From the tell-tale symptoms to detailed diagnostic tests and practical solutions, consider this your ultimate roadmap to restoring your Powerstroke’s legendary performance. Get ready to banish those frustrating
Quick Answers to Common Questions
How do I know if I’m having 7.3 Powerstroke fuel injector circuit issues?
You might notice rough idling, misfires, a significant loss of power, excessive smoke from the exhaust, or even a complete no-start condition. Often, your Check Engine Light will be on, showing specific diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) related to injector circuits.
What’s the very first thing I should check when diagnosing 7.3 Powerstroke fuel injector circuit issues?
Start by ensuring your batteries are fully charged and in good health, as low voltage can cause all sorts of electrical gremlins. Then, visually inspect the Injector Pressure Regulator (IPR) wiring and connections for any obvious damage or looseness.
Do I need special tools to diagnose 7.3 Powerstroke fuel injector circuit issues?
While a good quality multimeter is absolutely essential for testing continuity and voltage, a diagnostic scan tool capable of reading 7.3 Powerstroke-specific P-codes will be incredibly helpful for quickly pinpointing the exact 7.3 Powerstroke fuel injector circuit issues you’re facing.
Are 7.3 Powerstroke fuel injector circuit issues usually difficult to fix myself?
Many common 7.3 Powerstroke fuel injector circuit issues can be diagnosed and repaired by a competent DIYer with some patience and the right tools. However, some more complex electrical diagnostics might require professional expertise if you’re not comfortable with wiring.
What’s a common root cause for 7.3 Powerstroke fuel injector circuit issues?
Often, 7.3 Powerstroke fuel injector circuit issues stem from problems with the Under Valve Cover Harness (UVCH), which can become brittle and lose connection over time. Don’t forget to check the Injector Drive Module (IDM) connections and the main wiring harness for any signs of chafing.
📋 Table of Contents
- Understanding the 7.3 Powerstroke Injector System
- Common Symptoms of Fuel Injector Circuit Problems
- Essential Diagnostic Tools and Safety Precautions
- Step-by-Step Diagnostic Procedures for Fuel Injector Circuits
- Common 7.3 Powerstroke Injector Circuit Diagnostic Values
- Common Culprits and Their Solutions
- Preventative Maintenance and Best Practices
Understanding the 7.3 Powerstroke Injector System
Before we dive into troubleshooting, it’s crucial to understand how the 7.3 Powerstroke fuel injector system operates. Unlike common rail diesels, the 7.3 utilizes a Hydraulically Actuated Electronically Controlled Unit Injector (HEUI) system. This ingenious design uses engine oil pressure to atomize and inject fuel directly into the cylinders.

Learn more about How to fix 7.3 Powerstroke fuel injector circuit issues – How to Fix 7.3 Powerstroke Fuel Injector Circuit Issues: Diagnostic Guide
Image source: i.ytimg.com
How the 7.3 Injectors Work
In a HEUI system, the high-pressure oil pump (HPOP) generates up to 3,000 PSI of oil pressure. This high-pressure oil is routed to each injector, where it acts on an intensifier piston. The intensifier piston then pressurizes the fuel within the injector body to extreme levels (up to 21,000 PSI), forcing it through the nozzle and into the combustion chamber. The precise timing and duration of this injection are controlled electronically by the Injector Driver Module (IDM), which is instructed by the Powertrain Control Module (PCM).
| Common Issue/Symptom | Diagnostic Test | Expected Reading (Good) | Potential Fix |
|---|---|---|---|
| Misfire, rough idle, P02XX cylinder codes (single injector) | Ohms test injector solenoid at 42-pin UVCH connector (engine side) | 2.8-3.2 Ohms (between injector signal pins on connector). Open or very low indicates fault. | Replace faulty fuel injector(s) with open or shorted solenoid. |
| Intermittent misfire, multiple P02XX codes on one bank, often worse when hot | Visual inspection and continuity test of Under Valve Cover Harness (UVCH) and connector pins | No burnt, melted, or loose pins on UVCH connector. Solid continuity from 42-pin to injector. | Re-seat UVCH connectors; replace UVCH if pins are damaged or continuity is intermittent/lost. |
| No injector buzz test, no-start, P1316/P1317 (IDM codes) | Verify power & ground at IDM (Injector Driver Module) connector | KOEO: ~12V battery voltage (pins 1 & 2); < 0.1V on ground pins (14 & 15). | Check IDM fuses (30A, 20A), wiring to IDM. If power/grounds are good, replace IDM. |
| Intermittent engine cutout, random misfires, electrical short smell | Visual inspection of engine wiring harness for chafing (e.g., valve cover edges, frame rail) | No visible damage, exposed wires, or signs of abrasion on the main engine harness. | Repair or replace damaged sections of the engine wiring harness. Add protective conduit. |
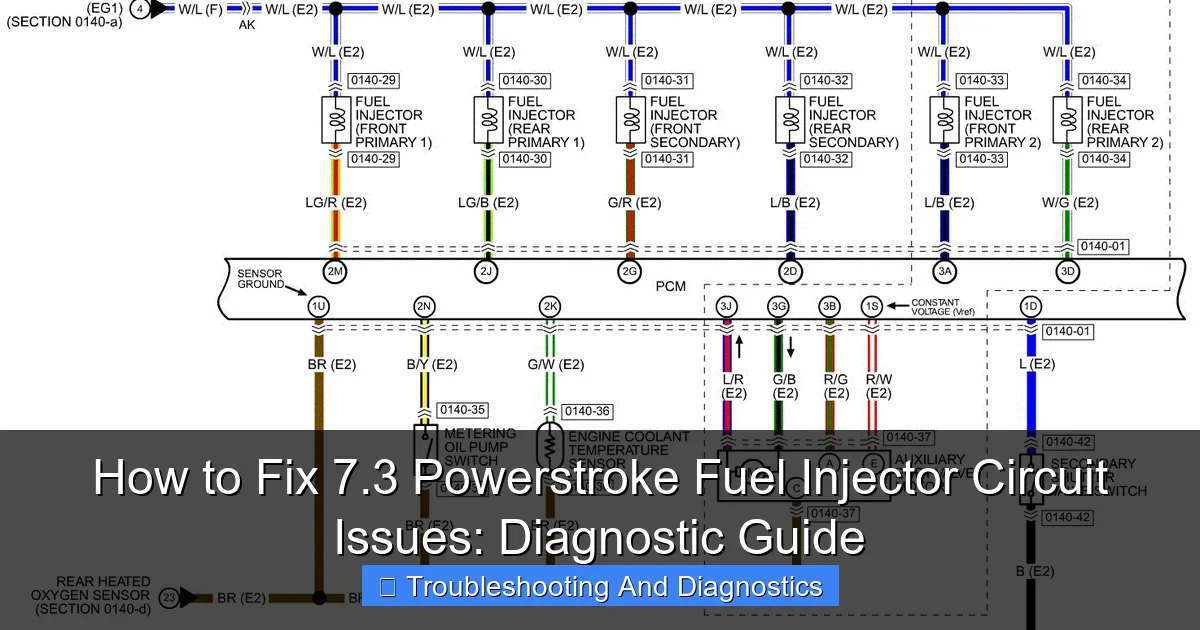
Key Components of the Injector Circuit
The entire electrical pathway for your injectors involves several critical components. Understanding each piece is vital when diagnosing 7.3 Powerstroke fuel injector circuit issues:
- PCM (Powertrain Control Module): The “brain” of your truck, it monitors various sensors and sends signals to the IDM to fire the injectors.
- IDM (Injector Driver Module): This module takes the low-voltage signals from the PCM and converts them into high-voltage pulses (typically 100-120V) required to actuate the injector solenoids. It’s often found on the driver’s side fender well.
- Main Engine Harness: This extensive wiring harness connects the PCM to the IDM and also carries signals from the IDM to the engine block, eventually reaching the Under Valve Cover (UVC) harness.
- UVC (Under Valve Cover) Harness: A common failure point! This harness resides under each valve cover, connecting the main engine harness to the individual injectors. It’s exposed to engine heat and oil, which contributes to its degradation over time.
- Fuel Injectors: Each injector contains a solenoid that, when energized by the IDM, opens a poppet valve, allowing high-pressure oil to actuate the injection process. An internal coil can short or open, leading to specific 7.3 Powerstroke fuel injector circuit issues.
Common Symptoms of Fuel Injector Circuit Problems
Recognizing the symptoms is the first step in diagnosing 7.3 Powerstroke fuel injector circuit issues. These problems can manifest in various ways, from mild annoyances to complete engine failure. If you experience any of these, it’s time to investigate:
Learn more about How to fix 7.3 Powerstroke fuel injector circuit issues – How to Fix 7.3 Powerstroke Fuel Injector Circuit Issues: Diagnostic Guide
Image source: rx8club.com
Engine Misfires and Rough Idle
One of the most immediate signs of a problem is a noticeable misfire, especially when the engine is cold or at idle. Your truck might shake excessively, and the exhaust note could sound uneven or “lumpy.” This indicates that one or more cylinders are not firing correctly due to a lack of fuel, often caused by an injector not receiving its firing signal.
Loss of Power and Poor Acceleration
If your 7.3 Powerstroke feels sluggish, struggles to accelerate, or lacks its usual pulling power, it could be a sign of multiple injectors failing or experiencing intermittent circuit issues. The engine isn’t receiving enough fuel to generate its full power output.
Hard Start or No Start Conditions
Perhaps the most alarming symptom, a hard start or complete no-start condition can often be traced back to 7.3 Powerstroke fuel injector circuit issues. If the injectors aren’t firing, or aren’t firing consistently, the engine won’t get the fuel it needs to ignite, regardless of cranking speed or fuel pressure.
Excessive Smoke from Exhaust
Depending on the nature of the injector circuit issue, you might see excessive smoke. White smoke often indicates unburnt fuel, which happens when an injector is stuck open or leaking, or not firing at all. Black smoke usually suggests over-fueling or inefficient combustion. Blue smoke is typically an oil issue, but a very worn injector can contribute to it.
Check Engine Light (CEL) and Specific Codes
The Check Engine Light is your truck’s way of telling you something is wrong. When dealing with 7.3 Powerstroke fuel injector circuit issues, you’ll often encounter specific Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs):
- P0201 – P0208: These codes indicate an open circuit in the injector control circuit for a specific cylinder (e.g., P0201 for cylinder 1, P0202 for cylinder 2, etc.).
- P1316: This crucial code signifies that the IDM has detected faults in the injector circuits and has stored its own codes. It’s a general indicator that you need to investigate the IDM and its associated wiring.
Essential Diagnostic Tools and Safety Precautions
Tackling 7.3 Powerstroke fuel injector circuit issues requires more than just a wrench. Having the right tools and adhering to strict safety protocols will make the job much easier and safer.
Tools You’ll Need
Equip yourself with the following:
- Digital Multimeter: Absolutely essential for testing resistance, continuity, and voltage. A good quality meter is paramount for accurate diagnosis.
- Scan Tool (with Powerstroke capabilities): A scan tool that can perform an injector “buzz test” and read IDM codes is invaluable. Generic OBD-II scanners may only give you P02XX or P1316; a more advanced tool can provide specific IDM fault codes.
- Test Light: Useful for quick power and ground checks.
- Torque Wrench: Critical for properly tightening valve cover bolts and other components to prevent leaks and damage.
- Socket and Wrench Set: For general disassembly and reassembly.
- Flathead and Phillips Screwdrivers: For various connections and covers.
- Dielectric Grease: To protect electrical connections from moisture and corrosion.
- Clean Rags/Shop Towels: For cleaning oil and grime.
- Gloves and Safety Glasses: Always protect your hands and eyes.
Safety First
Working on a diesel engine, especially its electrical and fuel systems, demands caution:
- Disconnect the Battery: Always disconnect both negative battery terminals before performing any electrical tests or working on wiring. This prevents accidental shorts and potential damage to the PCM or IDM.
- Beware of Hot Oil: Engine oil can be extremely hot. Allow the engine to cool down before removing valve covers.
- Fuel Pressure: While the 7.3’s fuel system is not as high-pressure as some modern diesels at the delivery side, always be mindful of fuel lines and potential spills.
- Moving Parts: Never work on the engine with it running, unless specifically instructed for a diagnostic step (like checking voltage). Keep hands clear of belts, fans, and other moving components.
- Cleanliness: Prevent dirt and debris from entering the fuel system or engine by keeping your work area clean.
Step-by-Step Diagnostic Procedures for Fuel Injector Circuits
Now, let’s get into the nitty-gritty of diagnosing those frustrating 7.3 Powerstroke fuel injector circuit issues. Follow these steps systematically to narrow down the problem.
Initial Visual Inspection
Start with the basics. Many issues can be found with a careful visual check:
- Check for Oil Leaks: Especially around the valve covers and IDM. Oil can wick into electrical connectors and cause shorts or poor connections.
- Inspect Connectors: Look at the main engine harness connectors for the IDM and at the valve cover pass-through connectors. Check for corrosion, bent pins, or signs of melting.
- Examine Wiring: Trace visible sections of the main engine harness and look for chafed, cut, or damaged wires. Pay close attention to areas where the harness might rub against engine components.
- Check Fuel and Oil Levels: Ensure your engine oil is at the correct level and that you have sufficient fuel. Low oil can mimic injector problems due to the HEUI system’s reliance on oil pressure.
Performing the “Buzz Test”
The buzz test is a fantastic diagnostic feature of the 7.3 Powerstroke. With a compatible scan tool, the IDM will cycle each injector solenoid rapidly, creating a distinct “buzzing” sound. This test helps identify open or shorted injector coils or circuit wiring without having to disassemble the engine.
- Connect your scan tool and navigate to the “Injector Buzz Test” function.
- Activate the test. Listen carefully to each injector. They should all make a clear, consistent buzzing sound.
- If an injector doesn’t buzz, or buzzes weakly, it indicates a problem with that injector’s coil or its associated wiring in the UVC harness. The scan tool may also provide specific cylinder fault codes during this test.
Under Valve Cover (UVC) Harness Inspection and Testing
This is where many 7.3 Powerstroke fuel injector circuit issues originate.
- Remove Valve Covers: Disconnect the negative battery terminals. Carefully remove the valve covers on the side(s) experiencing issues. You’ll see the UVC harness connecting to each injector and the main pass-through connector.
- Visual Inspection of UVC Harness: Look for cracked, brittle, or oil-soaked wires. Check for melted insulation or loose connections at the injectors.
- Injector Resistance Test (Cold):
- Disconnect the UVC harness from the injectors.
- Using your multimeter set to ohms (Ω), measure the resistance across the two pins of each injector’s solenoid.
- Expected Value: Around 2.8 to 3.2 Ohms (cold engine).
- Diagnosis: If you get a reading significantly higher (open circuit) or lower (short circuit), the injector coil is likely faulty and the injector needs replacement.
- UVC Harness Continuity Test:
- With the UVC harness disconnected from the injectors and the pass-through connector, use your multimeter on the continuity setting.
- Test continuity from the pins on the injector side of the harness to the corresponding pins on the pass-through connector.
- Expected Value: Very low resistance (near 0 Ohms).
- Diagnosis: Any high resistance or an open circuit indicates a faulty UVC harness, which is a very common failure point. Replacing the UVC harness is often a proactive repair for `7.3 Powerstroke fuel injector circuit issues`.
Main Engine Harness and IDM Circuit Testing
If the UVC harness and injectors test good, the problem might be upstream.
- IDM Connector Inspection: Unplug the main engine harness connector from the IDM. Inspect both sides for corrosion, bent pins, or signs of heat damage.
- Continuity from IDM Connector to Valve Cover Pass-through:
- You’ll need a wiring diagram for your specific year 7.3 Powerstroke to identify the correct pins.
- Test continuity from the IDM connector pins (output to injectors) to the pins on the valve cover pass-through connector (with the UVC harness disconnected).
- Expected Value: Very low resistance (near 0 Ohms).
- Diagnosis: High resistance or an open circuit indicates a damaged main engine harness.
- IDM Power and Ground Checks:
- With the IDM still disconnected, identify the power and ground wires at the IDM connector (refer to your wiring diagram).
- Reconnect the battery. Use your multimeter to check for battery voltage on the power wires and good continuity to ground on the ground wires.
- Diagnosis: No power or poor ground suggests fuse, relay, or main harness issues.
PCM and Injector Driver Module (IDM) Checks
The PCM and IDM work in tandem.
- IDM Input Signal: Using a specialized scope or advanced scan tool, you can monitor the low-voltage input signals from the PCM to the IDM. If these signals are missing or incorrect, it points to a PCM issue or wiring between the PCM and IDM.
- Swapping the IDM: If all other tests point to the IDM (especially if you have a P1316 code and known good injectors/harnesses), swapping it with a known good unit is often the quickest way to confirm. Be aware that many aftermarket IDMs can be unreliable, so consider a reputable remanufactured or new OEM unit.
Common 7.3 Powerstroke Injector Circuit Diagnostic Values
To further assist in your troubleshooting, here’s a table of common specifications and diagnostic values you’ll encounter when dealing with 7.3 Powerstroke fuel injector circuit issues. These are general guidelines; always refer to a specific factory service manual for the most precise values for your truck’s year and model, as minor variations can occur.
| Component/Test | Expected Value/Result | Diagnostic Implication (Out of Range) |
|---|---|---|
| Injector Resistance (Internal, Cold) | 2.8 – 3.2 Ohms | < 2.8 (short) or > 3.2 (open) Ohms suggests a faulty injector coil. |
| UVC Harness Continuity (Pin to Pin) | < 1 Ohm | High resistance or open circuit indicates a bad harness. |
| IDM Power Supply (Key On) | Battery Voltage (12V+) | No power: check fuses, relays, main harness connections. |
| IDM Output Voltage (to injectors, during buzz test or cranking) | ~100-120V Peak (pulse) | Low or no voltage suggests IDM or main harness issue. |
| Common DTCs (Scan Tool) | P0201-P0208, P1316 | P02XX points to specific cylinder circuit fault. P1316 indicates IDM codes stored (requires advanced scanner to retrieve IDM codes). |
| Engine Oil Level | Full, within range | Low oil or wrong oil viscosity can mimic injector issues by affecting HEUI operation. |
Common Culprits and Their Solutions
After going through the diagnostic steps, you’ll likely have a clearer picture of the root cause of your 7.3 Powerstroke fuel injector circuit issues. Here are the most common culprits and how to address them:
Failed UVC Harness (Under Valve Cover Harness)
The UVC harness is notoriously prone to failure. Exposed to constant heat cycles and engine oil, the insulation degrades, leading to shorts, opens, and intermittent connections. This is often the first place to look, especially for intermittent misfires that disappear when the engine is hot. A cracked harness can ground out on the valve cover or injector body.
- Solution: Replace the UVC harness. Always replace both sides if one is failing, as the other is likely not far behind. Opt for high-quality aftermarket or OEM replacements that are designed to withstand the harsh engine environment.
Faulty Injectors
Individual injectors can fail due to internal electrical shorts, open circuits in the solenoid coil, or mechanical wear (though mechanical issues are less about the circuit itself). An injector with an internal electrical fault will fail the resistance test and won’t buzz correctly.
- Solution: Replace the faulty injector. When replacing, consider the age and mileage of the other injectors. If one has failed, others might follow. For older, high-mileage engines, replacing all eight with new or thoroughly remanufactured units can be a long-term solution to avoid recurring 7.3 Powerstroke fuel injector circuit issues.
Defective Injector Driver Module (IDM)
The IDM is responsible for sending the high-voltage pulse to the injectors. If the IDM fails internally, it might stop sending pulses to one or more injectors, or it might fail completely, resulting in a no-start condition. A P1316 code is a strong indicator of an IDM issue.
- Solution: Replace the IDM. As mentioned, opt for a reputable, remanufactured, or new OEM unit to ensure reliability. Ensure all connections to the new IDM are clean and secure.
Damaged Main Engine Harness Wiring
While less common than UVC harness failure, the main engine harness can still suffer damage from chafing, heat, or rodent activity. This can lead to open circuits or shorts between the IDM and the valve cover pass-through connectors, causing specific cylinder misfires or general performance issues.
- Solution: Repair or replace the damaged section of the harness. If the damage is extensive or in multiple locations, replacing the entire engine harness might be necessary, though this is a more involved and costly repair.
Oil Contamination in Connectors
Oil can wick into electrical connectors, especially the main engine harness connector at the valve cover pass-through. This oil can degrade electrical conductivity, leading to intermittent problems or complete circuit failure.
- Solution: Disconnect, clean thoroughly with electrical contact cleaner, and apply dielectric grease to the connectors. Address any oil leaks causing the contamination to prevent recurrence.
Preventative Maintenance and Best Practices
Preventing 7.3 Powerstroke fuel injector circuit issues is always better than fixing them. A proactive approach can extend the life of your components and ensure your legendary engine continues to perform reliably.
Regular Maintenance Schedule
Adhering to your truck’s recommended maintenance schedule is paramount. This includes timely oil changes, fuel filter replacements, and general engine inspections. A well-maintained engine is less likely to develop unexpected electrical problems.
Quality Fuel Filters and Oil
The 7.3 Powerstroke’s HEUI system is sensitive to oil quality and cleanliness. Use only the recommended engine oil viscosity and always opt for high-quality, reputable fuel filters. Contaminated fuel or incorrect oil can put undue stress on the entire injection system, indirectly contributing to circuit issues.
Proactive UVC Harness Replacement
Given the UVC harness’s notorious failure rate, many experienced 7.3 Powerstroke owners recommend replacing it proactively, especially if you’re undertaking other work under the valve covers (like injector replacement) or if your truck has high mileage and the original harness. It’s a relatively inexpensive part that can save you significant diagnostic time down the road.
Monitoring for Early Symptoms
Pay attention to your truck’s behavior. Any subtle changes in idle quality, power delivery, or unusual exhaust smoke should be investigated promptly. Catching these 7.3 Powerstroke fuel injector circuit issues early can prevent more extensive damage or inconvenient breakdowns.
Troubleshooting 7.3 Powerstroke fuel injector circuit issues might seem daunting at first, but with the right approach and a little patience, it’s a completely manageable task for any dedicated Powerstroke owner. By understanding the system, using proper diagnostic tools, and following a systematic process, you can confidently identify and resolve these common problems.
Remember, the 7.3 Powerstroke is a testament to durability, and with a bit of TLC, it will continue to serve you faithfully for years to come. Don’t let a few electrical gremlins keep your beast sidelined. Embrace the challenge, follow this guide, and soon you’ll have your legendary truck thundering down the road with full power and efficiency once again. Happy wrenching!
🎥 Related Video: 7.3 P1316 Diagnosis – Troubleshooting and Repair of Injector/Glow Plug Harness
📺 Jason Frat
What to look for and how to solve P1316 code.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common symptoms of 7.3 Powerstroke fuel injector circuit issues?
You might experience a rough idle, misfires, a noticeable loss of power, excessive smoke from the exhaust, or even a complete cylinder dropout. The Check Engine Light will often illuminate, displaying codes related to injector circuit malfunctions.
What essential tools are needed to diagnose 7.3 Powerstroke fuel injector circuit problems?
A reliable multimeter is crucial for testing resistance and continuity within the circuit. A diagnostic scan tool capable of reading specific Powerstroke codes and performing an injector “buzz test” is also highly recommended for accurate diagnosis.
What are the most common causes of 7.3 Powerstroke fuel injector circuit failures?
The primary culprits are often a faulty Under Valve Cover Harness (UVCH), which can become brittle or corroded, and internal shorts or opens within the fuel injector solenoids themselves. Less commonly, issues with the Injector Driver Module (IDM) can also lead to circuit problems.
How do I start diagnosing a fault in my 7.3 Powerstroke fuel injector circuit?
Begin by connecting a diagnostic scan tool to pull any stored trouble codes, as these will often point you to a specific cylinder or circuit issue. Next, perform an injector “buzz test” to listen for each injector solenoid’s activation, which helps identify non-responsive injectors.
How can I specifically test individual 7.3 Powerstroke fuel injectors or their wiring?
You can use a multimeter to measure the resistance of each injector solenoid directly at the main engine harness connector or at the UVCH connector. A reading outside the specified range (typically 3.0-5.0 ohms) indicates a faulty injector or a wiring issue leading to it.
Is fixing 7.3 Powerstroke fuel injector circuit issues a DIY task, or should I seek professional help?
Basic diagnostic steps, such as pulling codes and performing resistance checks with a multimeter, are often manageable for a mechanically inclined DIYer. However, replacing injectors or diagnosing complex IDM issues may require more specialized tools and expertise, making professional assistance advisable for some repairs.






